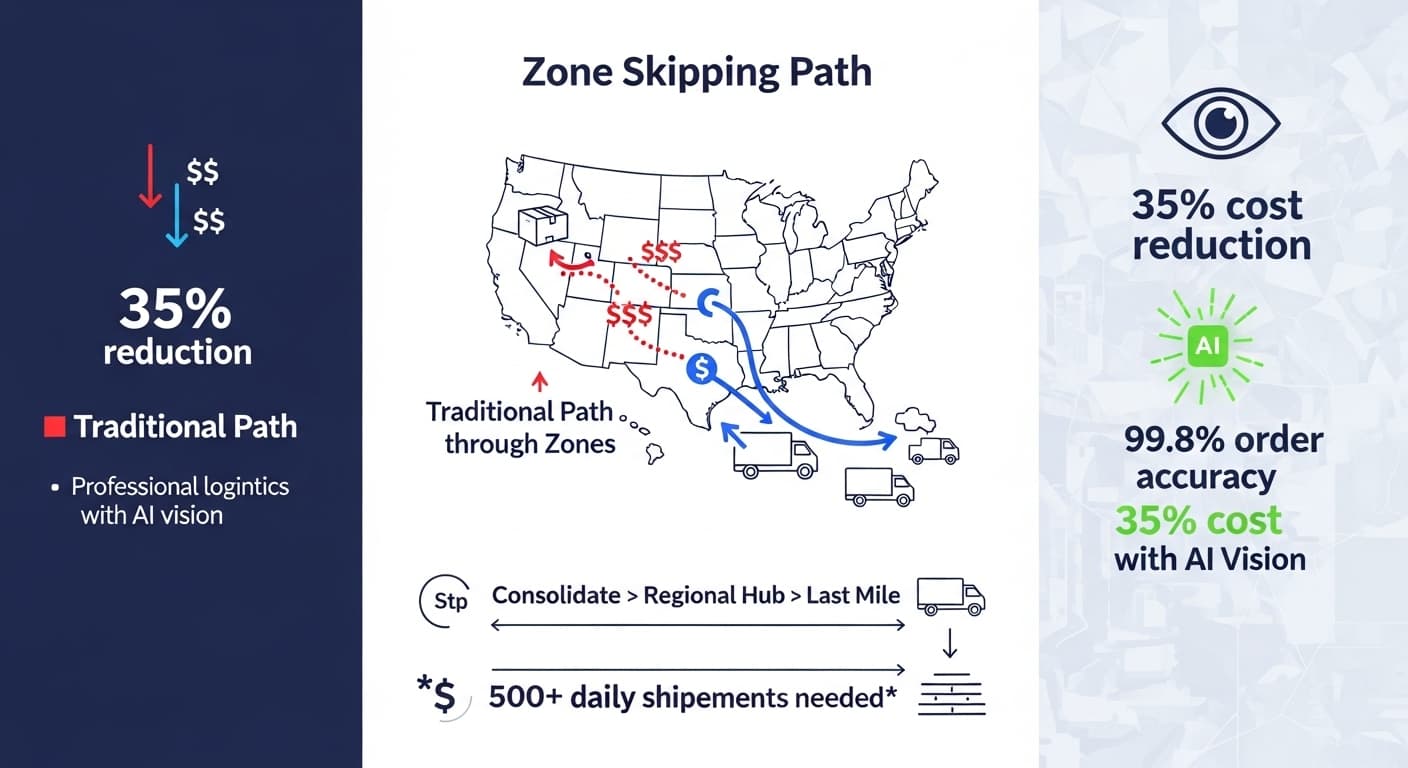
Executive Summary
Honda’s introduction of the Fastport eQuad platform represents a significant advancement in urban last-mile delivery technology. This comprehensive fleet-as-a-service solution combines zero-emission electric micro-mobility with intelligent software systems to address the growing challenges of urban logistics. Understanding the capabilities, implications, and strategic potential of this innovation is essential for logistics professionals, urban planners, and businesses seeking sustainable delivery solutions.
Honda’s Fastport eQuad: Pioneering the Future of Urban Last-Mile Delivery
(本田Fastport eQuad:引领城市末端配送的电动微出行革命)
1 · Understanding the Urban Delivery Revolution
The introduction of Honda’s Fastport eQuad platform on June 17, 2025, marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of urban logistics. This innovative approach to last-mile delivery addresses fundamental challenges that have long plagued urban distribution networks while introducing new possibilities for sustainable and efficient goods movement.
The Urban Logistics Challenge
Complexity of Modern Urban Delivery: Urban last-mile delivery has become increasingly complex as cities grow denser and consumer expectations continue to evolve:
Infrastructure Constraints:
- Traffic Congestion: Urban areas experience increasing traffic density that significantly impacts delivery efficiency
- Limited Parking: Scarce parking availability for traditional delivery vehicles creates operational challenges
- Access Restrictions: Growing number of pedestrian zones and vehicle access limitations in city centers
- Infrastructure Aging: Many urban areas have infrastructure that was not designed for current delivery volume demands
Economic Pressures:
- Cost Escalation: Last-mile delivery typically accounts for 30-50% of total logistics costs according to industry studies
- Labor Challenges: Driver shortages and increasing labor costs affecting service economics
- Fuel Volatility: Fluctuating fuel costs creating uncertainty in operational planning
- Customer Expectations: Demand for faster, more flexible delivery options while maintaining cost effectiveness
Environmental Considerations:
- Emission Regulations: Increasingly strict urban emission standards and low-emission zones
- Sustainability Mandates: Corporate and regulatory pressure for environmentally responsible delivery methods
- Air Quality Concerns: Public health considerations driving demand for cleaner delivery solutions
- Climate Goals: Municipal climate targets requiring significant reductions in transportation emissions
Market Evolution and Technology Convergence
Technological Enablers: Several technological developments have converged to make innovative solutions like the eQuad viable:
Battery Technology Advancement:
- Energy Density Improvements: Higher energy density batteries enabling practical electric micro-mobility solutions
- Swappable Systems: Development of standardized, swappable battery platforms reducing downtime
- Cost Reduction: Significant cost reductions in battery technology making electric solutions more economically viable
- Charging Infrastructure: Expanding charging and battery swap infrastructure supporting electric vehicle adoption
Software and Connectivity:
- Route Optimization: Advanced algorithms for optimizing delivery routes and schedules
- Fleet Management: Comprehensive software platforms for managing distributed vehicle fleets
- Real-Time Tracking: Enhanced tracking and communication capabilities improving service visibility
- Predictive Analytics: Data analytics for predicting demand patterns and optimizing resource allocation
Regulatory Environment:
- Micro-Mobility Recognition: Growing regulatory recognition and accommodation of micro-mobility solutions
- Incentive Programs: Government incentives for electric and sustainable transportation solutions
- Infrastructure Investment: Public investment in bicycle infrastructure that can support micro-mobility delivery
- Environmental Standards: Clear environmental standards providing market certainty for clean technologies
2 · Technical Innovation and Design Excellence
The Fastport eQuad represents a sophisticated integration of automotive engineering, electric propulsion technology, and urban mobility design principles that creates a uniquely capable delivery platform.
Advanced Electric Propulsion System
Mobile Power Pack (MPP) Technology: Honda’s MPP system represents a breakthrough in practical electric micro-mobility:
Swappable Battery Architecture: The MPP system provides several key advantages over fixed battery configurations:
- Operational Continuity: Ability to swap batteries in minutes rather than waiting hours for charging
- Fleet Efficiency: Centralized battery management and charging optimization across entire fleets
- Cost Optimization: Shared battery infrastructure reducing per-vehicle costs
- Scalability: Modular approach that can scale with business growth and changing needs
Performance Characteristics:
- Range Capability: Up to 23 miles per charge for the large model configuration
- Regenerative Braking: Energy recovery system extending operational range and improving efficiency
- Power Management: Intelligent power management optimizing performance across different operating conditions
- Environmental Resilience: Weather-resistant design ensuring reliable operation in various urban conditions
Intelligent Vehicle Design
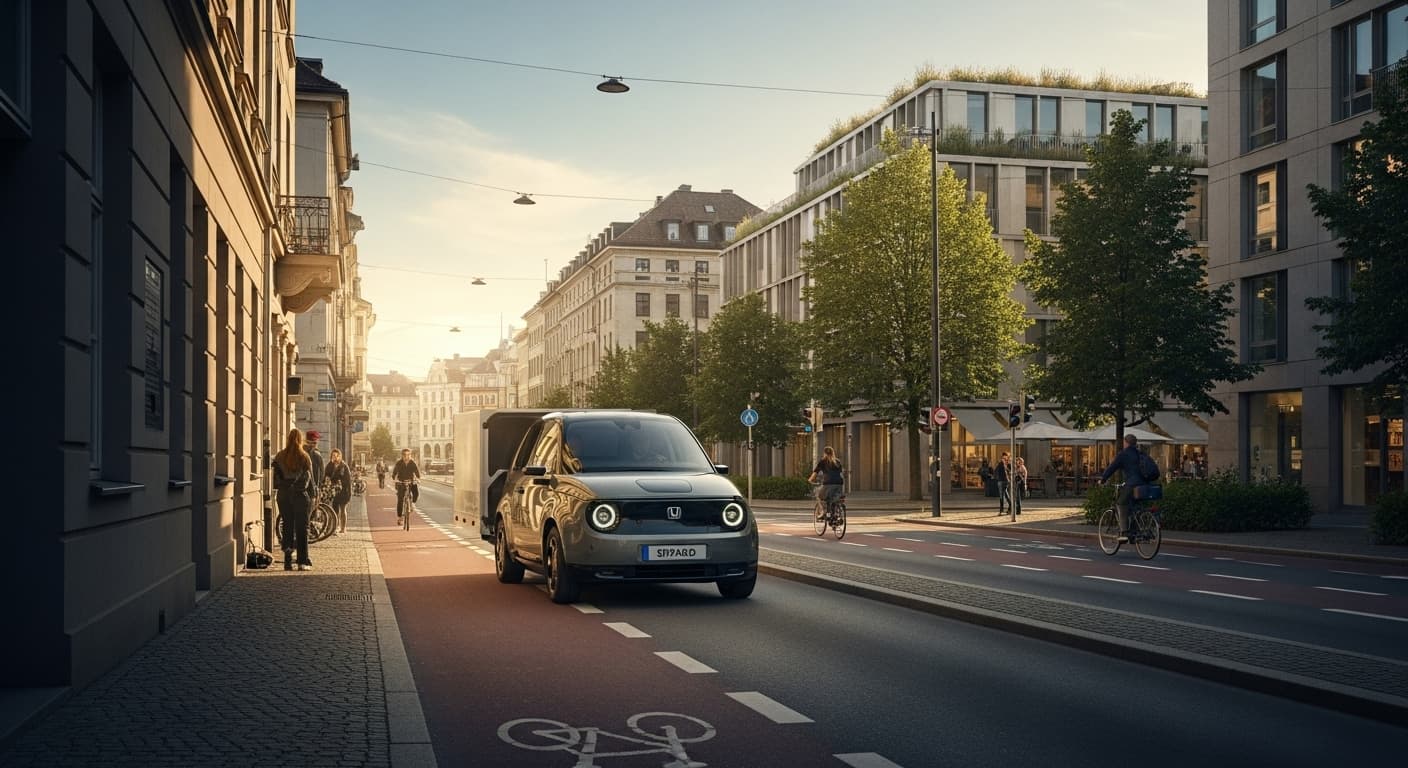
Urban-Optimized Configuration: The eQuad’s design reflects deep understanding of urban delivery requirements:
Size and Capacity Options:
- Large Model: 3.65 meters length with 295 kg payload capacity for high-volume routes
- Small Model: 3.4 meters length with 145 kg payload capacity for dense urban environments
- Modular Cargo Systems: Customizable cargo configurations supporting diverse delivery needs
- Accessibility Features: Design optimized for easy loading and unloading in constrained urban spaces
Safety and Operational Features:
- Pedal-by-Wire Assist: Advanced drivetrain providing precise control and energy efficiency
- Automatic Parking Brake: Safety system ensuring secure parking in urban environments
- Weather Protection: UV-coated canopy and sealed front enclosure protecting operator and cargo
- Ventilation System: Climate control features ensuring operator comfort during extended operations
Urban Mobility Optimization:
- Bicycle Lane Compatibility: 12 mph (20 km/h) top speed optimized for bicycle infrastructure use
- Maneuverability: Compact design enabling navigation through congested urban environments
- Stability: Four-wheel configuration providing stability advantages over two-wheel alternatives
- Noise Reduction: Electric propulsion eliminating noise pollution in urban environments
Software-Defined Vehicle Capabilities
Integrated Technology Platform: The eQuad incorporates advanced software systems that transform it from a simple vehicle into an intelligent delivery platform:
Fleet Management Integration:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vehicle location, performance, and operational status
- Route Optimization: AI-powered algorithms for optimizing delivery routes and schedules
- Performance Analytics: Comprehensive data collection and analysis for operational optimization
- Predictive Maintenance: Automated systems for predicting and scheduling maintenance needs
Over-the-Air Updates:
- Feature Enhancement: Ability to add new features and capabilities through software updates
- Performance Optimization: Continuous optimization of vehicle performance based on operational data
- Security Updates: Regular security updates ensuring protection against cyber threats
- Regulatory Compliance: Software updates ensuring compliance with evolving regulations
3 · Fleet-as-a-Service Model Innovation
Honda’s Fastport platform extends beyond vehicle manufacturing to encompass a comprehensive fleet-as-a-service model that addresses the full spectrum of urban delivery operational needs.
Comprehensive Service Architecture
Integrated Solution Framework: The Fastport FaaS model provides a complete ecosystem for urban delivery operations:
Vehicle and Equipment Services:
- Flexible Acquisition Options: Leasing and purchase options accommodating different business models and financial requirements
- Customization Services: Tailored cargo configurations and vehicle specifications for specific use cases
- Battery Management: Comprehensive battery swapping and charging infrastructure management
- Equipment Support: Full range of accessories and equipment to support diverse delivery applications
Technology and Software Services:
- Fleet Management Platform: Comprehensive software suite for managing all aspects of fleet operations
- Driver Interface Systems: User-friendly interfaces for drivers optimizing route execution and performance
- Customer Integration: APIs and integration capabilities for connecting with existing business systems
- Analytics and Reporting: Advanced analytics providing insights for operational optimization and business planning
Operational Support Services:
- Maintenance and Service: Comprehensive maintenance programs minimizing downtime and ensuring reliability
- Training Programs: Driver and fleet manager training ensuring optimal system utilization
- Technical Support: 24/7 technical support for addressing operational issues and questions
- Performance Optimization: Ongoing consultation and optimization services improving operational efficiency
Economic Value Proposition
Cost Structure Advantages: The FaaS model creates significant economic advantages over traditional delivery approaches:
Operational Cost Reduction:
- Fuel Elimination: Electric propulsion eliminating fuel costs and reducing exposure to price volatility
- Maintenance Simplification: Electric drivetrain reducing maintenance complexity and costs
- Insurance Optimization: Safety features and tracking capabilities potentially reducing insurance costs
- Parking and Access: Bicycle lane access reducing parking costs and access restrictions
Capital Efficiency:
- Reduced Capital Investment: FaaS model reducing upfront capital requirements for fleet deployment
- Asset Utilization: Shared infrastructure and services improving overall asset utilization
- Scalability: Ability to scale operations up or down based on demand without major capital commitments
- Technology Access: Access to advanced technology without the need for internal development or acquisition
Performance Benefits:
- Delivery Speed: Traffic avoidance through bicycle lane use improving delivery times
- Reliability: Electric propulsion and predictive maintenance improving operational reliability
- Flexibility: Modular design and software capabilities supporting diverse operational requirements
- Sustainability: Zero-emission operation supporting corporate sustainability goals and regulatory compliance
4 · Market Impact and Industry Transformation
The introduction of the Fastport eQuad platform has implications that extend beyond Honda’s immediate business objectives to encompass broader transformation in urban logistics and micro-mobility markets.
Addressing Critical Industry Pain Points
Urban Delivery Efficiency Crisis: The eQuad platform directly addresses several critical challenges facing the urban delivery industry:
Traffic Congestion Mitigation: Traditional delivery vehicles are severely impacted by urban traffic congestion, which continues to worsen in major metropolitan areas. The eQuad’s bicycle lane capability provides a fundamental advantage:
- Traffic Avoidance: Ability to bypass traffic congestion through dedicated bicycle infrastructure
- Predictable Transit Times: More consistent delivery schedules due to reduced traffic variability
- Route Flexibility: Access to routes and areas that may be restricted or impractical for larger vehicles
- Operational Efficiency: Reduced fuel costs and improved driver productivity through faster, more predictable routes
Environmental Compliance and Sustainability: Growing environmental regulations and corporate sustainability commitments are creating demand for cleaner delivery solutions:
- Zero Emission Operation: Complete elimination of local emissions supporting air quality improvements
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting increasingly strict urban emission standards and low-emission zone requirements
- Corporate Sustainability: Supporting corporate sustainability goals and environmental reporting requirements
- Public Health Benefits: Contributing to improved urban air quality and reduced noise pollution
Cost Structure Optimization: The high cost of last-mile delivery creates significant pressure for innovation:
- Labor Efficiency: Improved driver productivity through faster, more efficient routes
- Vehicle Utilization: Higher utilization rates due to improved operational efficiency
- Infrastructure Costs: Reduced infrastructure requirements compared to traditional delivery operations
- Energy Costs: Lower and more predictable energy costs compared to conventional fuel systems
Competitive Landscape Evolution
Market Positioning and Differentiation: Honda’s entry into urban delivery represents a significant development in the competitive landscape:
Automotive Industry Expansion: Traditional automotive manufacturers are expanding into new mobility markets:
- Technology Integration: Leveraging automotive engineering expertise in new applications
- Manufacturing Scale: Applying manufacturing scale advantages to micro-mobility solutions
- Brand Recognition: Utilizing established brand recognition and customer trust
- Distribution Networks: Leveraging existing dealer and service networks for new products
Competition with Specialized Providers: The eQuad platform competes with both traditional delivery methods and emerging micro-mobility solutions:
- Traditional Delivery Vehicles: Offering advantages in urban environments while maintaining payload capacity
- Bicycle and E-bike Solutions: Providing weather protection and higher payload capacity
- Delivery Drones: Offering immediate deployment without regulatory uncertainty
- Walking and Public Transit: Providing speed and capacity advantages for commercial applications
Partnership and Ecosystem Development: Success in urban delivery requires extensive partnership and ecosystem development:
- Logistics Company Partnerships: Collaboration with major logistics providers for fleet deployment
- Technology Integration: Partnerships with software and technology providers for enhanced capabilities
- Infrastructure Partnerships: Collaboration with cities and infrastructure providers for charging and battery swap networks
- Customer Integration: Working with retailers and e-commerce companies for integrated delivery solutions
5 · Pilot Programs and Real-World Validation
Honda’s approach to market development includes comprehensive pilot programs that provide valuable insights into real-world performance and operational requirements.
New York City Pilot Program Analysis
Urban Environment Testing: Honda’s completed pilot testing in New York City provides important validation of the eQuad’s capabilities in one of the world’s most challenging urban environments:
Operational Performance Validation:
- Traffic Navigation: Successful navigation of dense urban traffic through bicycle lane utilization
- Weather Resilience: Performance validation across different weather conditions and seasons
- Cargo Handling: Practical testing of loading, unloading, and cargo security in urban environments
- Safety Performance: Validation of safety systems and protocols in real-world operating conditions
Economic Performance Assessment:
- Cost Comparison: Direct comparison with traditional delivery methods in terms of total operational costs
- Productivity Measurement: Assessment of delivery productivity and efficiency compared to conventional approaches
- Utilization Analysis: Understanding of optimal utilization patterns and operational configurations
- Maintenance Requirements: Real-world assessment of maintenance needs and operational reliability
Stakeholder Feedback Integration:
- Driver Experience: Feedback from drivers regarding comfort, usability, and operational effectiveness
- Customer Reception: Assessment of customer acceptance and satisfaction with eQuad delivery service
- Regulatory Interaction: Experience with local regulations and permitting processes
- Community Impact: Understanding of community reception and urban integration
Expansion Strategy and Market Development
Geographic Expansion Planning: Honda is developing a systematic approach to market expansion based on pilot program learnings:
Market Selection Criteria:
- Urban Density: Focus on markets with sufficient density to justify micro-mobility solutions
- Regulatory Environment: Prioritizing markets with favorable regulatory frameworks for micro-mobility
- Infrastructure Readiness: Targeting markets with existing bicycle infrastructure and charging capabilities
- Customer Demand: Focusing on markets with strong demand for sustainable delivery solutions
Partnership Development Strategy:
- Logistics Provider Engagement: Working with major logistics companies for fleet deployment and operations
- Technology Integration: Partnerships with software providers for enhanced fleet management capabilities
- Infrastructure Development: Collaboration with charging and battery swap infrastructure providers
- Regulatory Engagement: Working with local governments on regulatory frameworks and pilot programs
6 · Technology Integration and Digital Transformation
The Fastport platform represents more than just an electric vehicle; it embodies a comprehensive approach to digital transformation in urban delivery operations.
Advanced Fleet Management Capabilities
AI-Powered Optimization Systems: The integration of artificial intelligence throughout the Fastport platform creates unprecedented capabilities for operational optimization:
Route Optimization and Dynamic Planning:
- Real-Time Traffic Integration: Continuous integration of traffic data for dynamic route optimization
- Delivery Window Optimization: AI algorithms optimizing delivery schedules based on customer preferences and operational constraints
- Capacity Utilization: Intelligent allocation of cargo space and vehicle capacity across delivery routes
- Weather Adaptation: Automatic adjustment of routes and schedules based on weather conditions and forecasts
Predictive Analytics and Performance Management:
- Demand Forecasting: Predictive models for anticipating delivery demand and resource requirements
- Maintenance Prediction: AI-powered systems for predicting maintenance needs and optimizing service schedules
- Performance Optimization: Continuous analysis of operational data for identifying improvement opportunities
- Cost Analysis: Comprehensive cost analysis and optimization across all aspects of fleet operations
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Comprehensive Performance Monitoring: The Fastport platform generates extensive data that provides unprecedented insights into urban delivery operations:
Operational Analytics:
- Delivery Performance Metrics: Detailed tracking of delivery times, success rates, and customer satisfaction
- Vehicle Utilization Analysis: Understanding of vehicle utilization patterns and optimization opportunities
- Driver Performance Management: Analytics supporting driver training, performance evaluation, and optimization
- Cost Analysis: Comprehensive cost tracking and analysis across all operational dimensions
Strategic Business Intelligence:
- Market Analysis: Data-driven insights into market opportunities and competitive positioning
- Customer Behavior Analysis: Understanding of customer preferences and delivery patterns
- Operational Efficiency Trends: Long-term analysis of operational efficiency and improvement trends
- ROI Analysis: Comprehensive return on investment analysis for different operational configurations
Integration with Existing Business Systems
Enterprise Integration Capabilities: The Fastport platform is designed to integrate seamlessly with existing business systems and workflows:
ERP and Business System Integration:
- Order Management Integration: Direct integration with existing order management and fulfillment systems
- Inventory Management: Real-time integration with inventory management systems for optimized delivery planning
- Customer Service Integration: Integration with customer service systems for enhanced delivery tracking and communication
- Financial System Integration: Seamless integration with accounting and financial management systems
Third-Party Service Integration:
- Payment Processing: Integration with payment systems for delivery confirmation and billing
- Customer Communication: Integration with customer communication platforms for delivery notifications and updates
- Tracking and Visibility: Integration with customer-facing tracking systems for enhanced visibility
- Quality Management: Integration with quality management systems for continuous improvement
7 · Sustainability Impact and Environmental Benefits
The environmental implications of the Fastport eQuad platform extend beyond simple emission reductions to encompass broader sustainability benefits and urban environmental improvement.
Comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment
Direct Environmental Benefits: The zero-emission operation of the eQuad creates immediate environmental benefits in urban environments:
Air Quality Improvement:
- Emission Elimination: Complete elimination of local air pollutants including NOx, particulates, and CO2
- Urban Air Quality: Direct contribution to improved urban air quality and public health
- Regulatory Compliance: Support for cities in meeting air quality standards and environmental regulations
- Health Benefits: Reduction in health impacts associated with urban air pollution
Noise Pollution Reduction:
- Quiet Operation: Electric propulsion significantly reducing noise pollution in urban environments
- Community Benefits: Improved quality of life in urban areas through reduced delivery-related noise
- Early Morning Operations: Ability to conduct deliveries during early morning hours without noise concerns
- Residential Area Operations: Enhanced ability to operate in noise-sensitive residential areas
Lifecycle Environmental Assessment
Comprehensive Sustainability Analysis: Understanding the full environmental impact requires analysis across the entire product lifecycle:
Manufacturing and Materials:
- Sustainable Materials: Use of recyclable and sustainable materials in vehicle construction
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Energy-efficient manufacturing processes reducing overall environmental impact
- Local Production: U.S. production reducing transportation-related emissions
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Sustainable practices throughout the supply chain
Operational Sustainability:
- Energy Efficiency: High energy efficiency reducing overall energy consumption
- Renewable Energy Integration: Compatibility with renewable energy sources for charging and operation
- Battery Lifecycle Management: Comprehensive battery recycling and lifecycle management programs
- Operational Optimization: Software-driven optimization reducing overall resource consumption
End-of-Life Considerations:
- Vehicle Recycling: Design for recyclability at end of vehicle life
- Battery Recycling: Comprehensive battery recycling programs for responsible end-of-life management
- Component Reuse: Design enabling reuse of components and materials
- Circular Economy Integration: Integration with circular economy principles and practices
8 · Economic Impact and Market Transformation
The introduction of the Fastport platform has broader economic implications that extend beyond Honda’s immediate business objectives to encompass job creation, economic development, and industry transformation.
Job Creation and Economic Development
Manufacturing and Production Impact: Honda’s commitment to U.S. production at the Performance Manufacturing Center in Ohio creates significant economic benefits:
Direct Employment Impact:
- Manufacturing Jobs: Creation of high-skilled manufacturing jobs in clean technology production
- Engineering and Design: Development of engineering and design capabilities in electric vehicle technology
- Supply Chain Development: Economic benefits throughout the supply chain supporting local suppliers and vendors
- Research and Development: Investment in R&D capabilities supporting long-term innovation and competitiveness
Economic Multiplier Effects:
- Local Economic Impact: Broader economic benefits in communities surrounding manufacturing facilities
- Technology Ecosystem: Development of technology ecosystems supporting innovation and entrepreneurship
- Skills Development: Investment in workforce development and skills training for emerging technologies
- Supplier Network: Development of supplier networks supporting the broader electric vehicle industry
Industry Transformation and Market Development
Catalyzing Industry Change: Honda’s entry into urban delivery represents a broader trend toward industry transformation:
Market Validation:
- Technology Viability: Demonstration of the commercial viability of electric micro-mobility solutions
- Business Model Innovation: Validation of fleet-as-a-service models in urban delivery applications
- Customer Acceptance: Market validation of customer acceptance for innovative delivery solutions
- Regulatory Pathway: Development of regulatory frameworks supporting micro-mobility deployment
Competitive Response and Innovation:
- Industry Innovation: Spurring innovation and development across the broader automotive and logistics industries
- Technology Advancement: Accelerating development of battery, software, and vehicle technologies
- Service Model Evolution: Encouraging development of new service models and business approaches
- Market Expansion: Creating opportunities for expansion of micro-mobility and sustainable transportation markets
Financial and Investment Implications
Investment and Capital Market Impact: The development of the Fastport platform reflects broader trends in investment and capital allocation:
Clean Technology Investment:
- Capital Allocation: Significant capital investment in clean technology development and deployment
- Technology Development: Investment in battery technology, software development, and manufacturing capabilities
- Infrastructure Investment: Investment in charging and battery swap infrastructure
- Market Development: Investment in market development and customer acquisition
Return on Investment Considerations:
- Long-Term Value Creation: Focus on long-term value creation rather than short-term financial returns
- Market Position: Investment in market position and competitive advantage
- Technology Leadership: Investment in technology leadership and intellectual property development
- Sustainability Leadership: Investment in sustainability leadership and environmental responsibility
9 · Future Outlook and Strategic Implications
Understanding the long-term implications of Honda’s Fastport platform requires consideration of broader trends in urban development, technology advancement, and transportation evolution.
Technology Evolution and Advancement
Continuous Innovation Pipeline: The Fastport platform represents an initial step in a broader technology evolution:
Battery Technology Advancement:
- Energy Density Improvements: Continued advancement in battery energy density enabling longer range and higher payload capacity
- Charging Speed Enhancement: Development of faster charging technologies reducing downtime and improving utilization
- Cost Reduction: Continued cost reductions in battery technology improving economic viability
- Sustainability Improvement: Enhanced sustainability in battery production and recycling
Software and AI Development:
- Algorithm Sophistication: Continued advancement in AI algorithms for route optimization and fleet management
- Integration Capabilities: Enhanced integration capabilities with existing business systems and infrastructure
- Predictive Analytics: More sophisticated predictive analytics for operational optimization
- Autonomous Capabilities: Potential development of autonomous delivery capabilities
Vehicle Design Evolution:
- Performance Enhancement: Continued improvement in vehicle performance, efficiency, and capability
- Customization Options: Expanded customization options for different applications and markets
- Safety Advancement: Enhanced safety features and systems
- User Experience: Improved user experience for both drivers and customers
Market Expansion and Geographic Development
Global Market Opportunities: The success of the Fastport platform in initial markets creates opportunities for global expansion:
International Market Development:
- European Markets: Expansion into European markets with strong environmental regulations and bicycle infrastructure
- Asian Markets: Development of Asian markets with high urban density and growing delivery demand
- Emerging Markets: Opportunities in emerging markets with growing urbanization and delivery needs
- Regulatory Harmonization: Development of international regulatory frameworks supporting global deployment
Application Diversification: Success in delivery applications creates opportunities for expansion into other applications:
- Passenger Transportation: Potential expansion into micro-mobility passenger transportation
- Service Applications: Applications in maintenance, repair, and other service industries
- Specialized Delivery: Specialized applications in healthcare, food service, and other industries
- Municipal Services: Applications in municipal services and government operations
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Integration
City Planning and Development: The widespread adoption of micro-mobility solutions like the eQuad has implications for urban planning and development:
Infrastructure Development:
- Bicycle Infrastructure Expansion: Increased investment in bicycle infrastructure to support micro-mobility solutions
- Charging Infrastructure: Development of comprehensive charging and battery swap infrastructure
- Traffic Management: Integration of micro-mobility considerations into traffic management and planning
- Zoning and Regulation: Evolution of zoning and regulatory frameworks to accommodate new mobility solutions
Smart City Integration:
- Traffic Optimization: Integration with smart city systems for traffic optimization and management
- Environmental Monitoring: Integration with environmental monitoring and air quality management systems
- Data Integration: Integration with city data systems for planning and optimization
- Service Coordination: Coordination with other city services and utilities
Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
For Urban Delivery Companies:
- Technology Evaluation: Systematic evaluation of micro-mobility solutions for specific operational requirements
- Pilot Program Development: Development of pilot programs to test and validate new delivery technologies
- Partnership Exploration: Exploration of partnerships with technology providers and vehicle manufacturers
- Sustainability Planning: Integration of sustainability considerations into long-term strategic planning
For Urban Planners and Policymakers:
- Infrastructure Planning: Consideration of micro-mobility infrastructure needs in urban planning processes
- Regulatory Framework Development: Development of regulatory frameworks supporting innovative delivery solutions
- Environmental Integration: Integration of delivery solutions into environmental and sustainability planning
- Economic Development: Consideration of micro-mobility manufacturing and services for economic development
For Technology and Vehicle Manufacturers:
- Market Opportunity Assessment: Systematic assessment of market opportunities in urban delivery and micro-mobility
- Partnership Development: Development of partnerships with logistics companies and urban delivery providers
- Technology Investment: Continued investment in battery, software, and vehicle technologies
- Service Model Development: Development of comprehensive service models supporting customer success
10 · Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Urban Mobility
Honda’s Fastport eQuad platform represents more than an innovative vehicle design; it embodies a comprehensive vision for transforming urban delivery through the integration of sustainable technology, intelligent software, and service-oriented business models.
Key Strategic Insights
Technology Integration Success: The Fastport platform demonstrates the potential for successful integration of multiple advanced technologies to create practical solutions for real-world challenges. The combination of electric propulsion, swappable battery technology, intelligent software systems, and comprehensive service support creates a solution that addresses the complexity of urban delivery operations.
Market Transformation Potential: The introduction of the eQuad platform has the potential to catalyze broader transformation in urban delivery markets. By demonstrating the viability of electric micro-mobility solutions and fleet-as-a-service models, Honda is creating opportunities for other companies to develop complementary solutions and for customers to adopt more sustainable delivery practices.
Sustainability Leadership: The zero-emission operation and comprehensive sustainability approach of the Fastport platform positions Honda as a leader in sustainable urban mobility. This leadership has implications not only for competitive positioning but also for contributing to broader environmental and public health goals in urban areas.
Long-Term Value Creation
Competitive Advantage Development: Organizations that successfully adopt and integrate innovative delivery solutions like the eQuad can develop sustainable competitive advantages through improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer service, and stronger environmental performance. Early adoption of these technologies positions companies for continued leadership as markets evolve.
Industry Evolution: The success of platforms like Fastport will likely accelerate broader evolution in the logistics and transportation industries. Companies that understand and adapt to these changes will be better positioned for long-term success in increasingly competitive and environmentally conscious markets.
Urban Development Impact: The widespread adoption of sustainable delivery solutions contributes to broader urban development goals including improved air quality, reduced traffic congestion, and enhanced quality of life. Organizations that align their operations with these broader goals create value not only for their immediate stakeholders but also for the communities they serve.
Future Considerations
Continuous Innovation: The rapid pace of technology advancement means that solutions like the Fastport platform represent steps in an ongoing innovation process rather than final destinations. Organizations that maintain focus on continuous improvement and adaptation will be best positioned to capture the benefits of ongoing technological advancement.
Ecosystem Development: Success in transforming urban delivery requires coordinated development across entire ecosystems including vehicles, infrastructure, regulations, and business models. Organizations that contribute to and benefit from ecosystem development will have advantages over those that focus solely on individual components.
Market Education and Adoption: The successful deployment of innovative solutions requires comprehensive market education and adoption support. Organizations that invest in helping customers understand and successfully implement new technologies will build stronger relationships and capture greater market opportunities.
The Honda Fastport eQuad platform represents a significant milestone in the evolution of urban delivery and micro-mobility solutions. Its success will depend not only on technological excellence but also on the ability to create comprehensive value for customers, communities, and the broader ecosystem of urban mobility stakeholders. Organizations that understand and engage with these developments will be better positioned to participate in and benefit from the transformation of urban transportation and delivery systems.
This comprehensive analysis examines Honda’s Fastport eQuad platform and its potential impact on urban delivery markets. The information presented is based on available technical specifications, industry analysis, and market trends. Organizations considering adoption of micro-mobility solutions or investment in urban delivery technology may benefit from consultation with experienced logistics and transportation professionals who can provide guidance tailored to specific operational requirements and market conditions.