Port of Los Angeles Sets Historic Record in July 2025: Strategic Analysis of the 1 Million TEU Milestone and Its Implications for U.S. Supply Chains
(洛杉矶港2025年7月创历史新高:100万TEU里程碑的战略分析与美国供应链影响)
Executive Summary
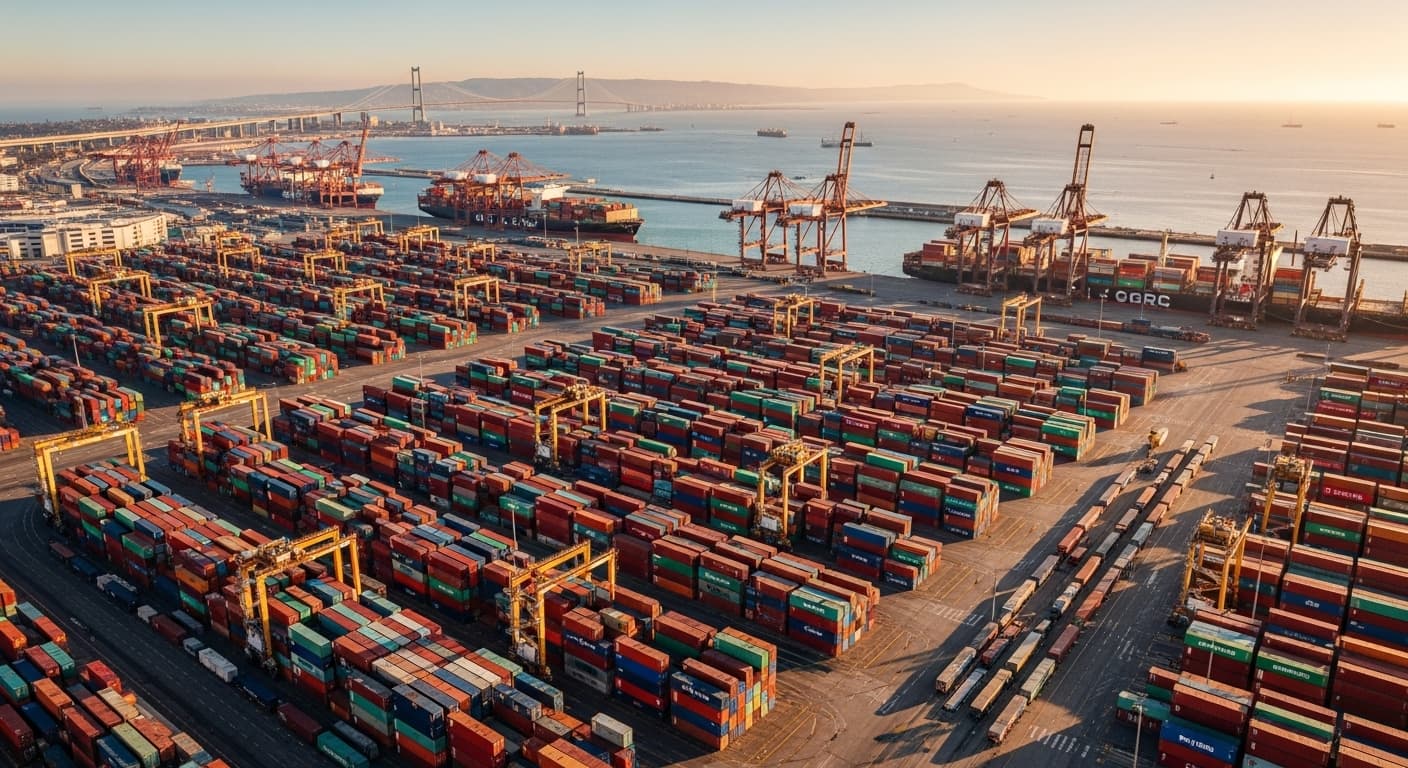
The Port of Los Angeles achieved an unprecedented milestone in July 2025, handling 1,019,837 twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs)—the highest monthly volume in the port’s 117-year history. This 8.5% year-over-year increase reflects a convergence of strategic importers frontloading cargo ahead of potential tariff changes, enhanced operational efficiency, and the port’s continued role as America’s premier gateway for international trade. This analysis examines the factors driving this historic achievement and its broader implications for supply chain strategy and trade policy.
The Historic Achievement: Breaking Through the Million-TEU Barrier
July 2025 marked a watershed moment for the Port of Los Angeles, as it became the first time in the port’s extensive history that monthly container volume exceeded the psychologically and operationally significant threshold of one million TEUs. This achievement represents more than just a numerical milestone—it demonstrates the port’s capacity to handle extraordinary volumes while maintaining operational efficiency.
Record-Breaking Performance Metrics
The July 2025 performance represented a substantial increase over the previous record of 944,232 TEUs set in July 2024, establishing new benchmarks across multiple operational categories:
Container Volume Breakdown:
- Total TEUs Processed: 1,019,837 (+8.5% year-over-year)
- Loaded Import Containers: 543,728 TEUs
- Loaded Export Containers: 121,507 TEUs (+6% year-over-year)
- Empty Container Repositioning: 354,602 TEUs (+10% year-over-year)
The substantial increase in empty container movements signals anticipation of continued high import volumes in subsequent months, as shipping lines position equipment to handle expected cargo flows. This forward-looking indicator suggests that the July surge may represent the beginning of a sustained period of elevated import activity rather than an isolated spike.
Historical Context and Significance
The Port of Los Angeles has been handling containerized cargo since 1959, making this 66-year journey to the million-TEU monthly threshold particularly meaningful. The achievement reflects not only the growth of international trade but also the port’s evolution into one of the world’s most sophisticated maritime logistics hubs.
Key Historical Milestones:
- 1959: Introduction of containerized cargo operations
- 2000: First time exceeding 500,000 TEUs in a single month
- 2018: Previous peak annual performance of 9.3 million TEUs
- 2024: Setting the stage with 944,232 TEUs in July
- 2025: Breaking the million-TEU barrier
This progression illustrates the port’s consistent growth trajectory and its ability to adapt infrastructure and operations to meet increasing demand from international trade.
Strategic Drivers Behind the Volume Surge
The unprecedented July performance resulted from a confluence of factors that created a perfect storm of import demand, demonstrating how trade policy uncertainty can drive immediate operational decisions with far-reaching supply chain implications.
Tariff Policy and Frontloading Strategies
The primary catalyst for July’s record performance was strategic frontloading by U.S. importers seeking to avoid potential tariff increases. This phenomenon demonstrates how trade policy uncertainty creates immediate behavioral changes throughout supply chains.
Timeline of Policy Developments:
- Early 2025: Signals of potential tariff reinstatement create planning urgency
- June 2025: Import acceleration as companies finalize frontloading strategies
- July 2025: Peak frontloading period with maximum cargo volumes
- Mid-July: 90-day extension announced, but cargo already in transit
- August 2025: Deadline pressure continues despite policy adjustments
Importer Response Patterns: Companies across multiple industries implemented frontloading strategies, each with distinct characteristics and operational implications:
Consumer Electronics: Technology companies accelerated imports of components and finished goods, particularly items subject to potential Section 301 tariffs. The complexity of electronics supply chains meant that companies needed to import not just finished products but also intermediate components for domestic assembly operations.
Apparel and Textiles: Fashion retailers and apparel importers brought forward seasonal inventory, recognizing that textile tariffs could significantly impact product pricing and competitive positioning. The seasonal nature of fashion merchandise added urgency to these decisions.
Home and Garden Products: Retailers in this category, particularly those serving the home improvement market, accelerated imports of tools, outdoor equipment, and seasonal items ahead of potential tariff implementation.
Operational Excellence Under Pressure
Despite processing unprecedented volumes, the Port of Los Angeles maintained operational efficiency without significant congestion or delays—a remarkable achievement that contrasts sharply with the bottlenecks experienced during the pandemic era.
Enabling Infrastructure and Process Improvements:
Advanced Gate Systems: Implementation of truck appointment systems and automated gate processes reduced dwell times and improved traffic flow throughout the port complex.
Rail Integration Enhancement: Improved coordination between marine terminals and rail operators facilitated faster cargo movement inland, preventing the accumulation of containers at terminal facilities.
Digital Cargo Tracking: Enhanced visibility systems allowed beneficial cargo owners (BCOs) and logistics providers to track container status in real-time, enabling better planning and coordination.
Collaborative Planning: Systematic coordination between ocean carriers, terminal operators, and inland transportation providers ensured that capacity was aligned with demand patterns.
Executive Director Gene Seroka emphasized this operational success: “Terminals in July were jam-packed with ships loaded with cargo, processed without any delay—much to the credit of our dedicated longshore workers, terminal and rail operators, truckers, and supply chain partners.”
This operational resilience represents years of investment in infrastructure modernization and process improvement, positioning the port to handle extraordinary volumes while maintaining service standards.
Broader Implications for Supply Chain Strategy
The July surge at the Port of Los Angeles provides valuable insights into broader trends affecting supply chain management, trade policy, and strategic planning for international businesses.
Frontloading as Risk Mitigation Strategy
The widespread use of frontloading strategies demonstrates how companies are adapting to an environment of increased trade policy volatility. While effective for avoiding immediate tariff impacts, frontloading creates both opportunities and challenges for supply chain management.
Strategic Benefits of Frontloading:
- Cost Certainty: Locking in current tariff rates and avoiding potential increases
- Inventory Security: Ensuring product availability during uncertain policy periods
- Competitive Positioning: Potential advantage over competitors who delay imports
- Customer Service: Maintaining inventory levels to support customer demand
Operational Challenges and Costs:
- Increased Working Capital Requirements: Higher inventory investments strain cash flow
- Warehousing Capacity Pressure: Need for additional storage space during surge periods
- Demand Distortion: Artificial acceleration of imports followed by potential slowdowns
- Risk Concentration: Higher exposure to inventory obsolescence and market changes
Long-term Strategic Considerations: Companies implementing frontloading strategies must balance short-term risk mitigation with long-term operational efficiency. Successful implementation requires sophisticated demand forecasting, inventory management, and financial planning capabilities.
Impact on Freight Markets and Logistics Capacity
The cargo surge created ripple effects throughout the logistics ecosystem, demonstrating the interconnected nature of modern supply chains and the importance of capacity planning across multiple transportation modes.
Ocean Freight Market Effects:
- Capacity Utilization: Near-100% utilization of vessel space on trans-Pacific routes
- Rate Pressure: Upward pressure on spot ocean freight rates due to high demand
- Equipment Shortages: Temporary shortages of containers and chassis in some markets
- Service Priority: Carriers prioritizing high-volume customers and premium services
Inland Transportation Impacts:
- Rail Capacity Strain: Increased demand for intermodal rail services to move containers inland
- Trucking Market Pressure: Higher demand for drayage services and over-the-road transportation
- Warehouse Utilization: Near-capacity utilization of distribution centers in key markets
- Labor Market Effects: Increased demand for logistics workers across multiple sectors
Infrastructure Utilization: The surge tested the capacity limits of integrated transportation infrastructure, highlighting both strengths and potential bottlenecks in the U.S. logistics network.
Connection to Broader Trade Trends
The Port of Los Angeles surge reflects several macro-level trends reshaping international trade patterns and supply chain strategies.
Section 321 De Minimis Changes: The pending elimination of the $800 de minimis threshold for certain imports is driving consolidation of small shipments into formal entries, concentrating more cargo flows through major ports like Los Angeles.
Tariff Mitigation Strategies: Companies are implementing sophisticated tariff avoidance and mitigation strategies, including classification engineering, origin diversification, and value-chain restructuring, which can affect port selection and cargo routing decisions.
E-commerce Evolution: The continued growth of e-commerce and direct-to-consumer shipping models is changing the nature of imports, with implications for port operations and inland distribution strategies.
Supply Chain Regionalization: While companies maintain global supply chains, there’s increasing emphasis on regional resilience and risk diversification, affecting trade flows and port utilization patterns.
Industry Analysis and Competitive Positioning
The record performance at the Port of Los Angeles provides insights into competitive dynamics among U.S. ports and the evolving landscape of maritime logistics.
West Coast Port Competition
The Los Angeles achievement occurs within a competitive environment among West Coast ports, each seeking to attract cargo and provide superior service to importers and logistics providers.
Port of Long Beach: As Los Angeles’s adjacent neighbor, Long Beach also experienced increased volumes during the same period, though specific numbers vary. The two ports together form the San Pedro Bay port complex, the largest container port complex in the Western Hemisphere.
Port of Oakland: Northern California’s primary container port saw more modest increases, as geographic factors and infrastructure constraints limit its ability to handle the largest vessel calls that increasingly dominate trans-Pacific trade.
Pacific Northwest Ports: Seattle and Tacoma experienced varying levels of volume increase, with some cargo potentially shifting to Southern California ports due to capacity and service considerations.
Strategic Differentiation Factors:
- Infrastructure Capacity: Ability to handle ultra-large container vessels (ULCV)
- Rail Connectivity: Quality and capacity of rail connections to inland markets
- Terminal Efficiency: Productivity metrics and operational reliability
- Inland Access: Highway connectivity and congestion management
- Service Networks: Availability of logistics services and distribution facilities
Implications for Shippers and Logistics Providers
The July surge demonstrates both the opportunities and challenges facing companies that depend on efficient cargo movement through West Coast ports.
Benefits for Supply Chain Efficiency:
- Proven Capacity: Demonstration that the port can handle extraordinary volumes
- Operational Reliability: Maintained service levels despite record throughput
- Infrastructure Investment: Evidence of successful infrastructure modernization
- Industry Coordination: Effective collaboration among supply chain stakeholders
Planning Considerations for Importers:
- Capacity Reservations: Need for advance planning and capacity reservations during peak periods
- Alternative Routing: Development of contingency plans using multiple ports and routes
- Inventory Strategy: Integration of port performance into inventory planning and risk management
- Service Provider Selection: Evaluation of logistics providers based on port access and capability
Technology and Process Innovation: The successful handling of record volumes highlights the importance of technology adoption and process innovation in modern port operations, providing lessons for other facilities and supply chain participants.
Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
The Port of Los Angeles’s historic July performance provides a foundation for analyzing future trends and strategic considerations affecting port operations and supply chain management.
Short-term Market Dynamics
Policy Resolution Timeline: The resolution of tariff policy uncertainty will significantly affect cargo flows in the remainder of 2025. Extended policy uncertainty may lead to continued volatility in import patterns.
Peak Season Overlap: The traditional peak season for imports (August through October) overlapping with policy-driven frontloading could create unprecedented capacity pressures across the logistics network.
Inventory Normalization: Companies that frontloaded inventory may reduce imports in subsequent months, potentially creating a cyclical pattern of high and low volume periods.
Capacity Investment Decisions: The demonstrated ability to handle extreme volumes may influence infrastructure investment decisions by port authorities, terminal operators, and logistics providers.
Long-term Strategic Implications
Infrastructure Planning: The July performance provides valuable data for long-term infrastructure planning, including berth capacity, rail connections, and inland distribution facilities.
Technology Adoption: The successful handling of record volumes demonstrates the value of technology investment in port operations, potentially accelerating adoption of automation and digital management systems.
Supply Chain Resilience: The experience reinforces the importance of supply chain resilience and the ability to handle extraordinary circumstances while maintaining operational effectiveness.
Trade Pattern Evolution: Long-term trade patterns may be influenced by companies’ experiences during this period, potentially affecting future port selection and supply chain design decisions.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
Trade Policy Framework: The relationship between trade policy uncertainty and operational decisions highlights the need for predictable policy frameworks that enable effective business planning.
Infrastructure Investment: Federal and state infrastructure investment policies may be influenced by demonstrations of capacity utilization and economic impact.
Environmental Compliance: Continued volume growth must be balanced with environmental sustainability goals and regulatory requirements.
International Competitiveness: The port’s performance affects U.S. competitiveness in international trade and the attractiveness of the U.S. market for global suppliers.
Lessons for Supply Chain Management
The Port of Los Angeles’s record July offers several key lessons for supply chain professionals and business leaders navigating an increasingly complex global trade environment.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Policy Risk Assessment: Companies must develop sophisticated capabilities for assessing and responding to trade policy risks, including scenario planning and contingency development.
Operational Flexibility: The importance of maintaining operational flexibility to respond to sudden changes in demand patterns, regulatory requirements, or market conditions.
Capacity Planning: The need for comprehensive capacity planning that considers not just normal operations but also extraordinary circumstances and surge requirements.
Stakeholder Coordination: The value of effective coordination among all supply chain stakeholders, from ocean carriers to inland transportation providers.
Strategic Planning Integration
Trade Policy Integration: Supply chain strategy must explicitly incorporate trade policy considerations and potential scenarios into planning processes.
Infrastructure Investment: The importance of continued investment in infrastructure and technology to maintain competitiveness and operational effectiveness.
Performance Measurement: Development of comprehensive performance metrics that capture both efficiency and resilience under various operating conditions.
Continuous Improvement: The need for ongoing process improvement and adaptation to changing market conditions and operational requirements.
Technology and Innovation Adoption
Digital Integration: The critical role of digital technologies in enabling coordination and visibility across complex supply chain networks.
Automation Benefits: The value of automation in maintaining performance under high-volume conditions while managing labor constraints.
Data Analytics: The importance of sophisticated data analytics for demand forecasting, capacity planning, and performance optimization.
Collaborative Platforms: The need for collaborative technology platforms that enable effective coordination among multiple stakeholders.
Industry Best Practices and Recommendations
Based on the analysis of the Port of Los Angeles’s record performance, several best practices emerge for supply chain management and operational excellence.
For Importers and Beneficial Cargo Owners
Strategic Diversification: Develop diversified port and transportation strategies that provide flexibility and risk mitigation while maintaining operational efficiency.
Advance Planning: Implement sophisticated planning processes that can anticipate and respond to policy changes, seasonal patterns, and market dynamics.
Technology Investment: Invest in technology systems that provide real-time visibility and enable rapid decision-making in response to changing conditions.
Partnership Development: Cultivate strong relationships with logistics service providers, including ocean carriers, port operators, and inland transportation companies.
For Logistics Service Providers
Capacity Management: Develop flexible capacity management strategies that can scale to meet extraordinary demand while maintaining service quality.
Technology Integration: Invest in technology platforms that enable seamless integration with customer systems and provide comprehensive visibility.
Performance Excellence: Focus on operational excellence and reliability as key differentiators in a competitive market environment.
Risk Management: Develop comprehensive risk management capabilities that address operational, financial, and regulatory risks.
For Port Authorities and Terminal Operators
Infrastructure Investment: Continue investing in infrastructure modernization and expansion to meet growing demand and changing operational requirements.
Process Optimization: Implement continuous improvement processes that enhance efficiency and reliability while accommodating volume growth.
Stakeholder Collaboration: Foster collaborative relationships among all stakeholders in the port ecosystem to optimize overall performance.
Technology Leadership: Lead in the adoption of new technologies that enhance operational capability and competitive positioning.
Conclusion: Strategic Insights for Supply Chain Excellence
The Port of Los Angeles’s achievement of processing over one million TEUs in July 2025 represents more than a statistical milestone—it demonstrates the complex interplay between trade policy, operational excellence, and strategic supply chain management in today’s interconnected global economy.
Key Strategic Takeaways
Policy-Driven Volatility: Trade policy uncertainty creates immediate operational challenges and opportunities, requiring sophisticated risk management and contingency planning capabilities.
Operational Resilience: Investment in infrastructure, technology, and process improvement enables organizations to handle extraordinary circumstances while maintaining service excellence.
Supply Chain Integration: Success requires effective coordination among all stakeholders in complex supply chain networks, from international suppliers to final customers.
Strategic Flexibility: Organizations that maintain strategic flexibility and operational adaptability are better positioned to respond to changing market conditions and policy environments.
Future Considerations
The lessons learned from this historic achievement provide valuable guidance for navigating an increasingly complex and dynamic global trade environment. As companies continue to grapple with trade policy uncertainty, supply chain disruptions, and evolving customer expectations, the ability to manage extraordinary circumstances while maintaining operational excellence becomes increasingly critical.
The Port of Los Angeles’s success demonstrates that with proper planning, investment, and coordination, supply chain organizations can meet extraordinary challenges while continuing to provide reliable, efficient service. This experience provides a roadmap for building resilient, adaptive supply chains capable of thriving in an uncertain global environment.
Understanding these dynamics and their implications is essential for supply chain professionals, business leaders, and policy makers working to build more efficient, resilient, and competitive supply chain networks. The strategic insights gained from analyzing this historic achievement can inform decision-making across the logistics industry and contribute to continued improvement in supply chain performance and reliability.
The analysis of port performance trends and supply chain dynamics requires deep understanding of logistics operations, trade policy implications, and strategic planning considerations. Organizations seeking to optimize their supply chain strategies or navigate complex trade policy environments may benefit from professional guidance from experienced logistics and supply chain specialists who can provide insights tailored to specific operational requirements and strategic objectives.